Dependency Vulnerability Risk Calculation
DevGuard employs a risk calculation algorithm to assess and prioritize dependency vulnerabilities in your projects. This approach goes beyond standard CVSS scoring by incorporating additional threat intelligence and contextual factors to provide a more accurate risk assessment.
Essential is, that the risk scores are intend to support your remediation prioritization efforts by highlighting vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk to your applications, but do not represent absolute measurements of risk, nor do they account for all possible environmental factors specific to your deployment. Even a low-risk vulnerability may be critical in certain contexts, and vice versa.
DevGuard recalculates vulnerability risks several times per day as new threat intelligence becomes available. You can configure webhooks to receive real-time notifications when risk scores change, and if you have issue tracker synchronization enabled (GitLab, GitHub, or Jira), changes will be automatically reflected in your tickets.
Risk Calculation Formula
DevGuard uses the following formula to calculate the risk score for each vulnerability:
Risk = ((CVSS Environmental Score with Threat Metrics × (EPSS + 1)) / 2) / Component DepthThis formula balances three critical dimensions:
- Base vulnerability severity (CVSS Score)
- Adjusted CVSS score with environmental and threat metrics
- Exploit probability (EPSS)
- Impact surface (Component Depth)
Risk Factors Explained
CVSS Score
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides the foundation for risk assessment. Incorporating infromation about the technical severity of a vulnerability based on several metrics:
- Attack Vector: Network-based, adjacent network, local, or physical access
- Attack Complexity: How difficult the vulnerability is to exploit
- Privileges Required: Whether attackers need special access rights
- User Interaction: Whether user action is required for exploitation
- Scope: Whether the vulnerability can affect resources beyond its security scope
- Impact Metrics:
- Confidentiality: Potential for unauthorized information disclosure
- Integrity: Potential for unauthorized data modification
- Availability: Potential for service disruption
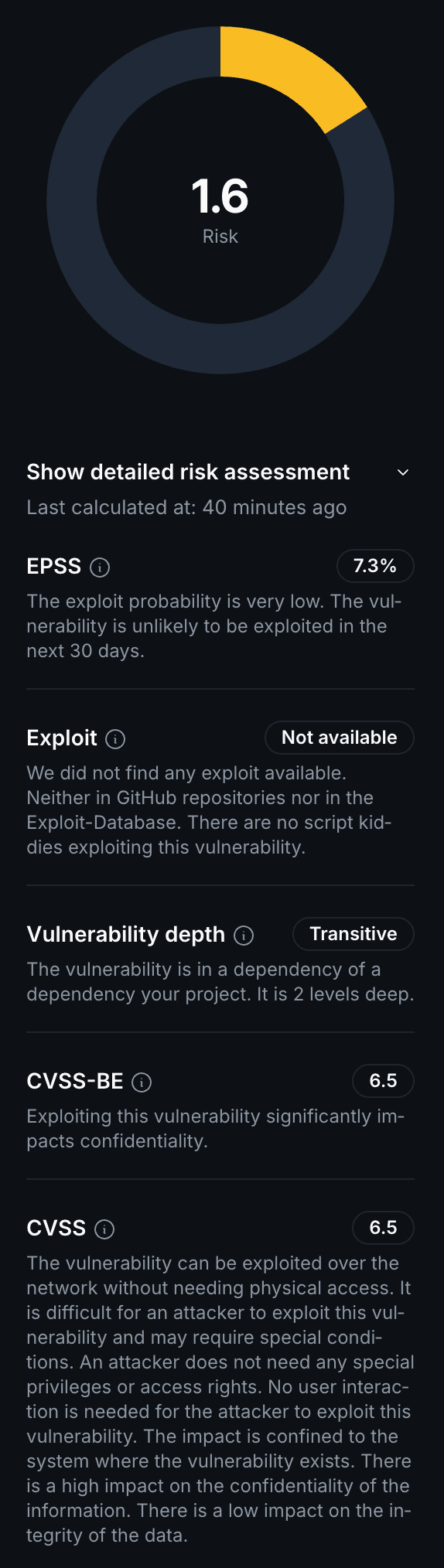
Example: A CVSS score of 6.5 might indicate a network-exploitable vulnerability with low complexity, requiring no privileges or user interaction, with high confidentiality impact and low integrity impact.
CVSS-BE (Base + Environmental)
DevGuard adjusts the base CVSS score using environmental metrics to reflect your specific deployment context.
- You can customize your security requirements in your repository settings (confidentiality, integrity, availability).
This adjustment ensures the risk score reflects real-world impact in your infrastructure, not just theoretical vulnerability severity.
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System)
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System uses machine learning and threat intelligence to estimate the probability of a vulnerability being exploited in the next 30 days. EPSS scores range from 0% to 100%.
Example: An EPSS score of 7.3% indicates a low exploit probability, meaning the vulnerability is unlikely to be targeted by attackers in the near future, even if technically exploitable.
Exploit Availability
DevGuard actively scans multiple sources to determine if working exploits exist:
- GitHub Repositories: Public exploit code and proof-of-concepts
- Exploit Database: Curated collection of publicly available exploits
The absence of available exploits substantially reduces the practical risk, as exploitation requires attacker effort and expertise.
Vulnerability Depth (Component Depth)
The depth of a vulnerable dependency in your project’s dependency tree impacts the probability of actually being affected by a vulnerable function. The risk formula divides by component depth, recognizing that deeper dependencies are:
- Less likely to be exploitable through your application
- Harder to trigger malicious code paths
- Often isolated by abstraction layers
Data Sources and Continuous Monitoring
DevGuard’s risk calculation leverages the Aggregated Vulnerability Database, which consolidates data from over 22 sources including:
- NVD (National Vulnerability Database)
- OSV (Open Source Vulnerabilities)
- EPSS (First.org)
- GitHub Security Advisories
- Exploit Database
- Multiple ecosystem-specific databases
Continuous Updates: DevGuard recalculates risk scores multiple times daily as new threat intelligence arrives. This ensures your risk assessments remain current with the evolving threat landscape.
Notifications and Integrations
Webhook Notifications
Configure webhooks to receive real-time notifications when:
- New vulnerabilities are discovered in your dependencies
- Risk scores change due to new threat intelligence
Issue Tracker Synchronization
When issue tracker synchronization is enabled for your project (GitLab, GitHub, or Jira) you get:
- Automatically created and updated issues for vulnerabilities
- Management via slash commands
- Notifcations of status changes directly through your issue tracker
Changes to risk scores and vulnerability status are automatically reflected in synchronized tickets, ensuring your team always works with current information.
Best Practices
- Prioritize by Risk Score: Focus remediation efforts on high-risk vulnerabilities first
- Consider Context: Review environmental factors specific to your deployment
- Monitor Trends: Track how risk scores change over time as threat landscape evolves
- Automate Notifications: Set up webhooks and issue tracker sync for timely awareness
- Regular Reviews: Periodically reassess accepted risks as new intelligence emerges
Related Documentation
- Aggregated Vulnerability Database - Learn about DevGuard’s comprehensive data sources
- Software Composition Analysis - Understand how DevGuard identifies vulnerabilities
- Ingesting Upstream Information - Bring your own suppliers data and assessment documents